General Overview of EU FMD
With the Falsified Medicines Directive (FMD) published in July 2011, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) set the beginning of traceability standards of the countries in the European Union.
The Falsified Medicines Directive (Directive 2011/62/EU) introduces harmonized European measures to fight medicine falsifications and ensure that medicines are safe and that medicines in trade circulation are strictly controlled. Measures include:
- Obligatory safety features – a unique identifier and an anti-tampering device – on the outer packaging of medicines
- A common, EU-wide logo to identify legal online pharmacies
- Tougher rules on the import of active pharmaceutical ingredients
- Strengthened record-keeping requirements for wholesale distributors
As of 2019, all of the pharmaceutical products have to fully meet the FMD obligations. Until 2025, EU countries with a separate system such as Greece and Italy must be fully compliant with the pharmaceutical track and trace regulation.
Serialization Requirements
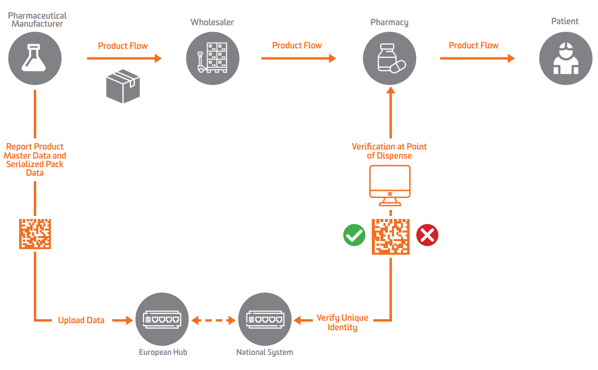
According to EU FMD, serialization must appear at the secondary or saleable-unit level in Europe. To enable verification, manufacturers need to first serialize product and send that serialized data to a central repository that can perform queries against it.
To enable serialization, verification, and reporting to Authorities, EU FMD requires that manufacturers mark packages with four data elements that must be printed in human readable form, and encoded and stored in a GS1 2D DataMatrix:
- Product identifier
- Serial number
- Lot or batch number
- Expiry date
The use of the fifth data element — the national reimbursement number — is optional, and few states in the EU may request to include the same in unique identifier to link the reimbursement of a drug product under a socialised medicine programme.
Pharmaceutical manufacturers and parallel traders must report data to a central EU Hub run by the European Medicines Verification Organization (EMVO), which also onboard users into the Hub. This will push data down to appropriate data repositories run by corresponding National Medicines Verification Organizations (NMVOs), which are responsible for end-user onboarding and for the operation of the national systems.
Reporting Requirements
Under EU FMD, Marketing Authorization Holder (MAH) is required to submit product master data and serialized product pack data.
Master data includes:
- Product codes
- Form
- Strength
- Doses per pack
- Pack type
- Target market(s) for distribution
- Future and any updates to product master data
Serialized product pack data includes:
- Product codes
- Lot/batch number
- Expiry date
- Serial numbers
- Any updates to serialized product pack data
